Lymphocyte antigen 6G
Neutrophils play a key role in tumorigenesis with both pro-and anti-tumorigenic properties.
To study the effects of neutrophils in vivo, one method that can be used is to deplete the neutrophils, which can be achieved either through the use of knockdown models, or depleting antibodies.
Lymphocyte antigen 6G (Ly6G) is highly expressed on neutrophils and is part of the Granulocyte Receptor (Gr-1).
Knockout models have been created for related proteins (e.g., Csf3r, Cxcr2, Gfi-1) to eliminate neutrophils, however they are not always ideal as either there can be only partial depletion of mature neutrophils, or protein targets also affect other cell types that can include monocytes and mast cells 1, which may require bone marrow transplants to rectify for some experiments.
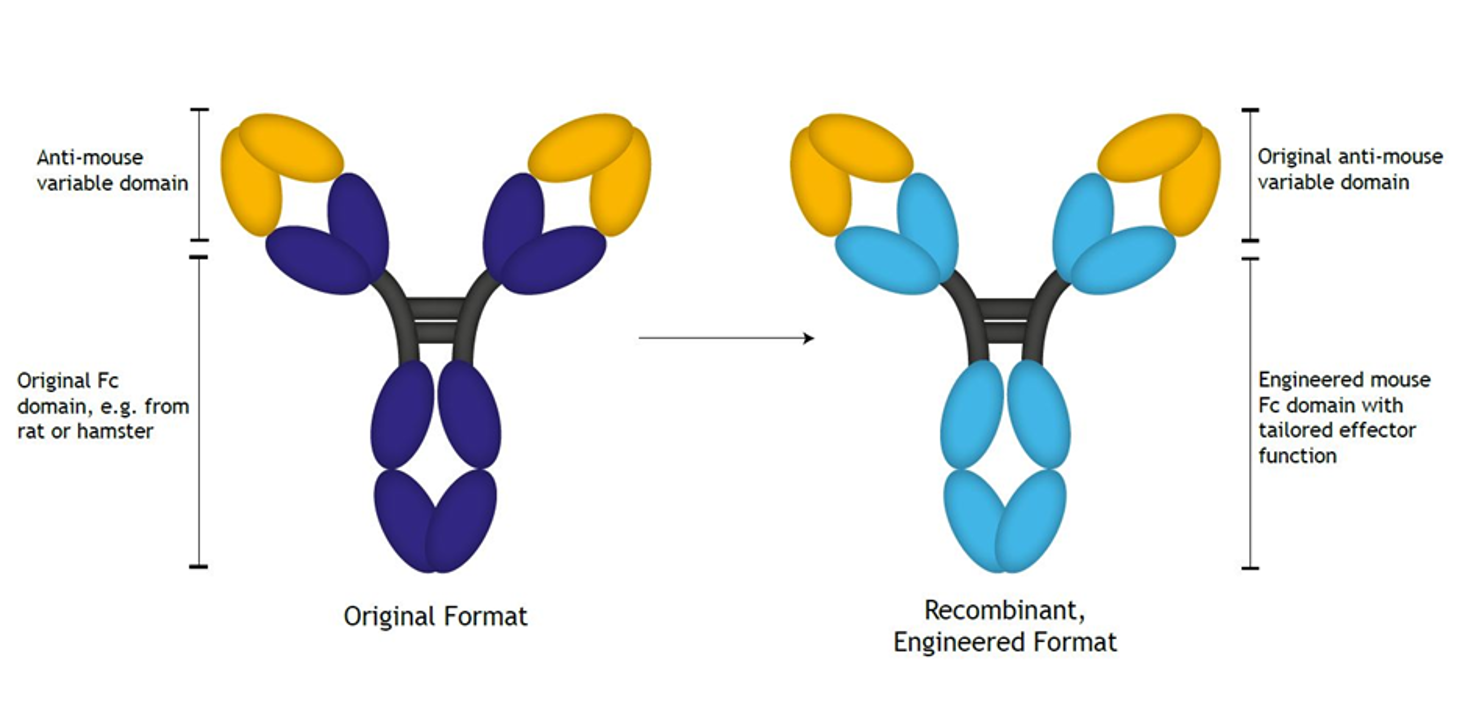
Depletion antibodies from closely related species can be used in vivo for short term experiments, however anti-depletion antibodies can be produced over time that reduces the efficacy as depletion antibodies are cleared by the host more swiftly.
Gr-1 depleting Rat IgG2b antibody clone RB6-8C5 has been advantageous for studies as it kills neutrophils more swiftly than targeting with rat IgG2a derived clone 1A8 for Ly-6G as they activate different pathways. However Gr-1 antibodies also recognise epitopes on subsets of monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells so Ly-6G allows for selective depletion of neutrophils in vivo.
Through isotype switching, recombinant versions of antibodies can be made that offer the specificity of established targets but with reduced immunogenicity in vivo, and this longer clearance times. Selection of the IgG2a isotype is also beneficial as it can bind all murine Fcγ receptors, but with low affinity for inhibitory receptors enabling the antibody to induce antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity , antibody-dependent phagocytosis as well as complement-dependent cytotoxicity for swift, selective neutrophil depletion in longer running experiments. 2
References
1. Stackowicz Julien, Jönsson Friederike, Reber Laurent L. Mouse Models and Tools for the in vivo Study of Neutrophils, Frontiers in Immunology 10 2020 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2019.03130 DOI=10.3389/fimmu.2019.03130 1664-3224
2. Olofsen, Patricia A., Marjolein C. Stip, J. H. Marco Jansen, Chilam Chan, Maaike Nederend, Ralph G. Tieland, Maria Tsioumpekou, and Jeanette H. W. Leusen. 2022. "Effective, Long-Term, Neutrophil Depletion Using a Murinized Anti-Ly-6G 1A8 Antibody" Cells 11, no. 21: 3406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213406