Superoxide Dismutase Monomers
Product Sizes
100 ug
SPR-435-100UG
2 x 100 ug
SPR-435-2X100UG
5 x 100 ug
SPR-435-5X100UG
About this Product
- SKU:
- SPR-435
- Additional Names:
- Superoxide dismutase1 Protein Monomer, ALS1 Protein Monomer, SOD1 Protein Monomer, IPOA Protein Monomer
- Application:
- Cell-based/Functional Assay, SDS-PAGE, Western Blot
- CE/IVD:
- RUO
- Extra Details:
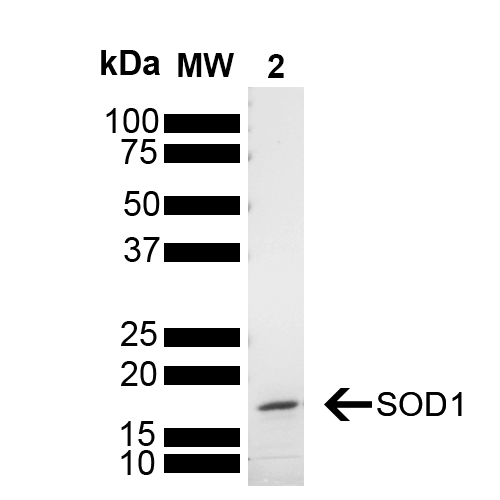
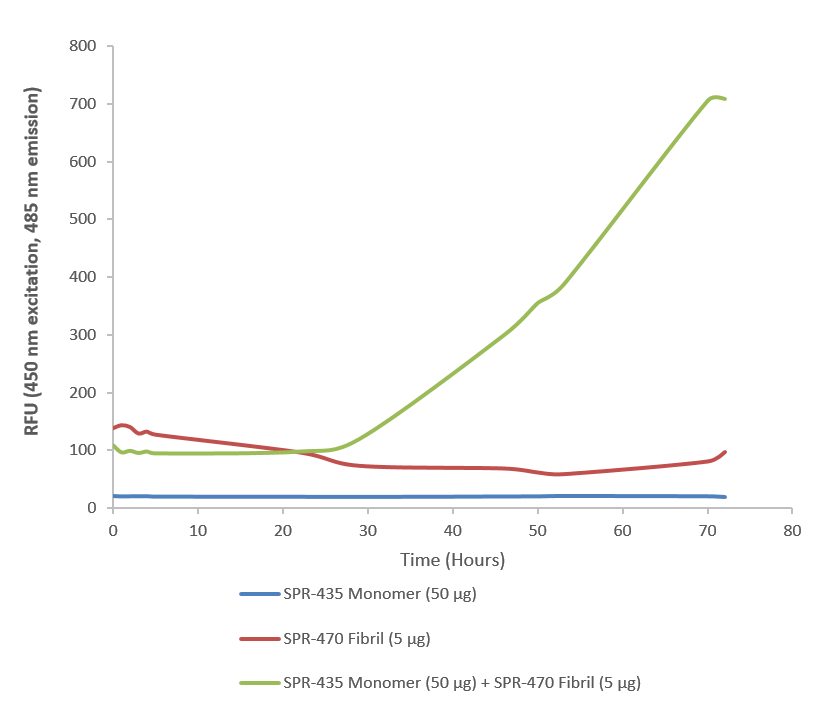
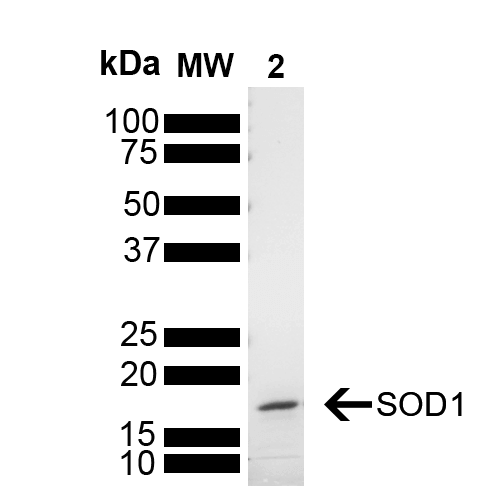
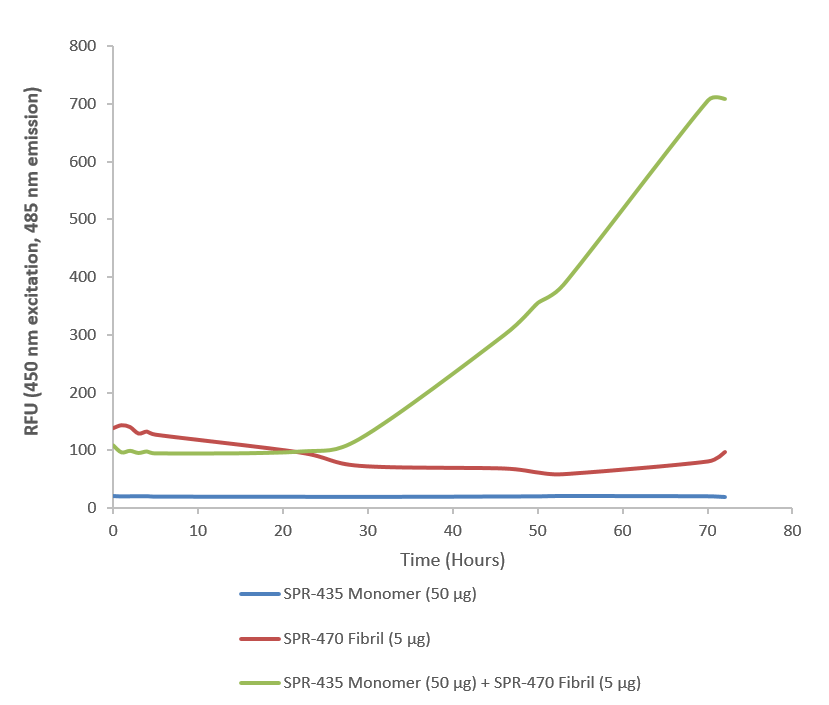
- Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is an endogenously produced intracellular enzyme present in almost every cell in the body (3). It works by catalyzing the dismutation of the superoxide radical O2 to O2 and H2O2, which are then metabolized to H2O and O2 by catalase and glutathione peroxidase (2,5). In general, SODs play a major role in antioxidant defense mechanisms (4). There are two main types of SOD in mammalian cells. One form (SOD1) contains Cu and Zn ions as a homodimer and exists in the cytoplasm. The two subunits of 16 kDa each are linked by two cysteines forming an intra-subunit disulphide bridge (3). The second form (SOD2) is a manganese containing enzyme and resides in the mitochondrial matrix. It is a homotetramer of 80 kDa. The third form (SOD3 or EC-SOD) is like SOD1 in that it contains Cu and Zn ions, however it is distinct in that it is a homotetramer, with a mass of 30 kDA and it exists only in the extra-cellular space (7). SOD3 can also be distinguished by its heparin-binding capacity (1). Studies have shown that in vitro, Cu-Zn SOD (SOD1) fibrils are transduced into cells and function as seeds to trigger the aggregation of endogenously expressed SOD1 (9).
- Immunogen:
- Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)
- Molecular Weight:
- 15.936 kDa
- Purity:
- >95%
- Purification:
- Ion Exchange
- Shipping Conditions:
- Dry Ice
- Storage Conditions:
- -70[o]C
- Supplier:
- StressMarq Biosciences
- Type:
- Proteins, Peptides, Small Molecules & Other Biomolecules: Recombinant Proteins
- Manufacturer's Data Sheet:https://www.stressmarq.com/products/proteins/sod-protein-spr-435/