Crystallography and Cryo-EM
Crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) are important and techniques play a vital part in structural biology research. The understanding of this field has undergone significant advancements, allowing researchers to determine the 3D structures of macromolecules at atomic resolution. Understanding these structures provides valuable insights into the function of biological molecules, assisting in a range of downstream applications including drug discovery, protein engineering, and the development of novel therapeutics.
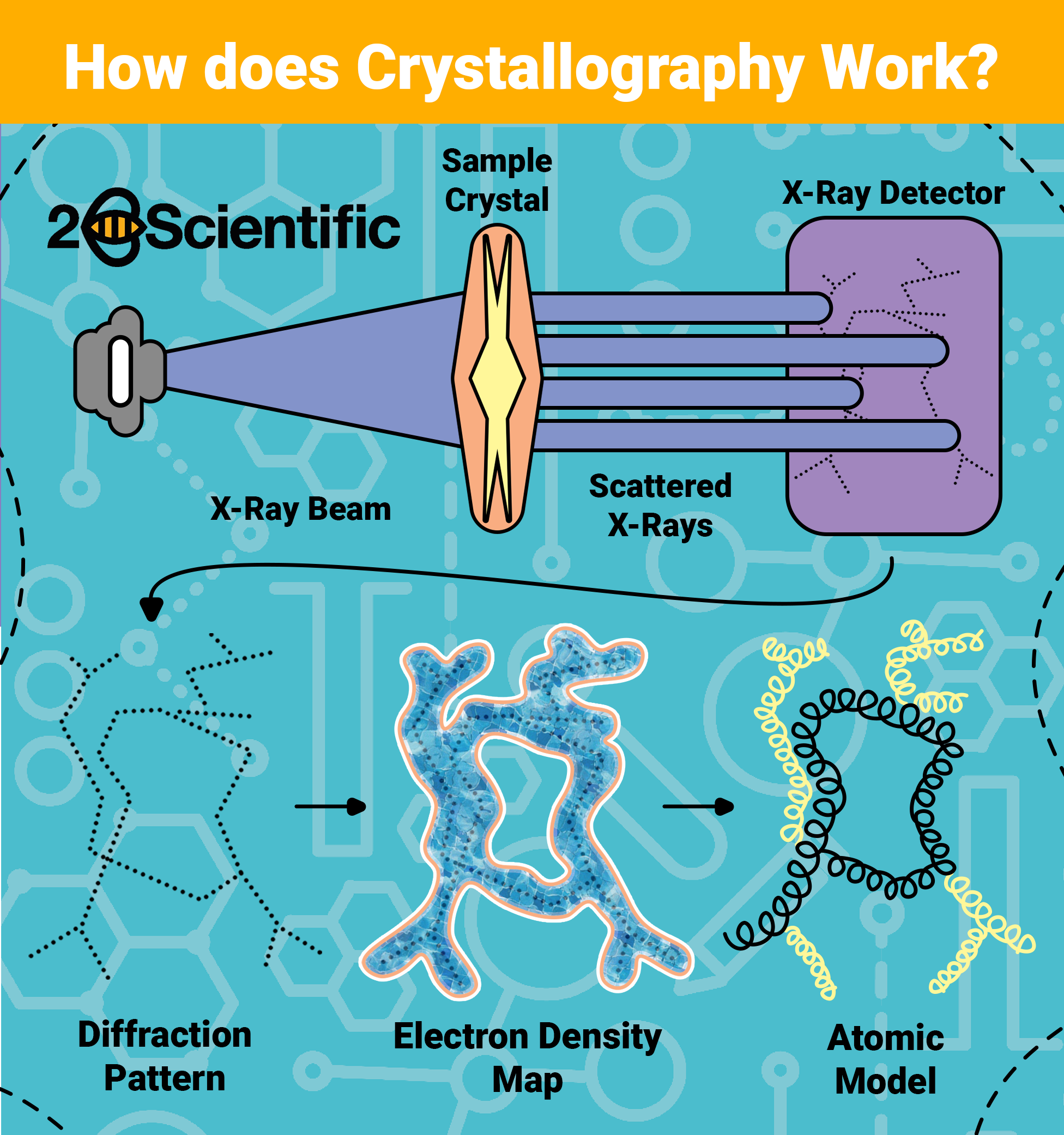
Crystallography
The process starts with crystallising a substance and then bombarding the crystal with X-rays. The X-rays are diffracted into specific patterns, which are collected on a detector. These patterns are mathematically transformed into a three-dimensional map of electron density, revealing the positions of atoms within the crystal.
The benefits of crystallography for research include providing detailed atomic-level structural information, which is essential for understanding the properties and functions of molecules. This information is crucial for drug design, discovering new materials, and improving material performance. Crystallography is widely used in chemistry, biology, and advance our understanding of molecular structures.
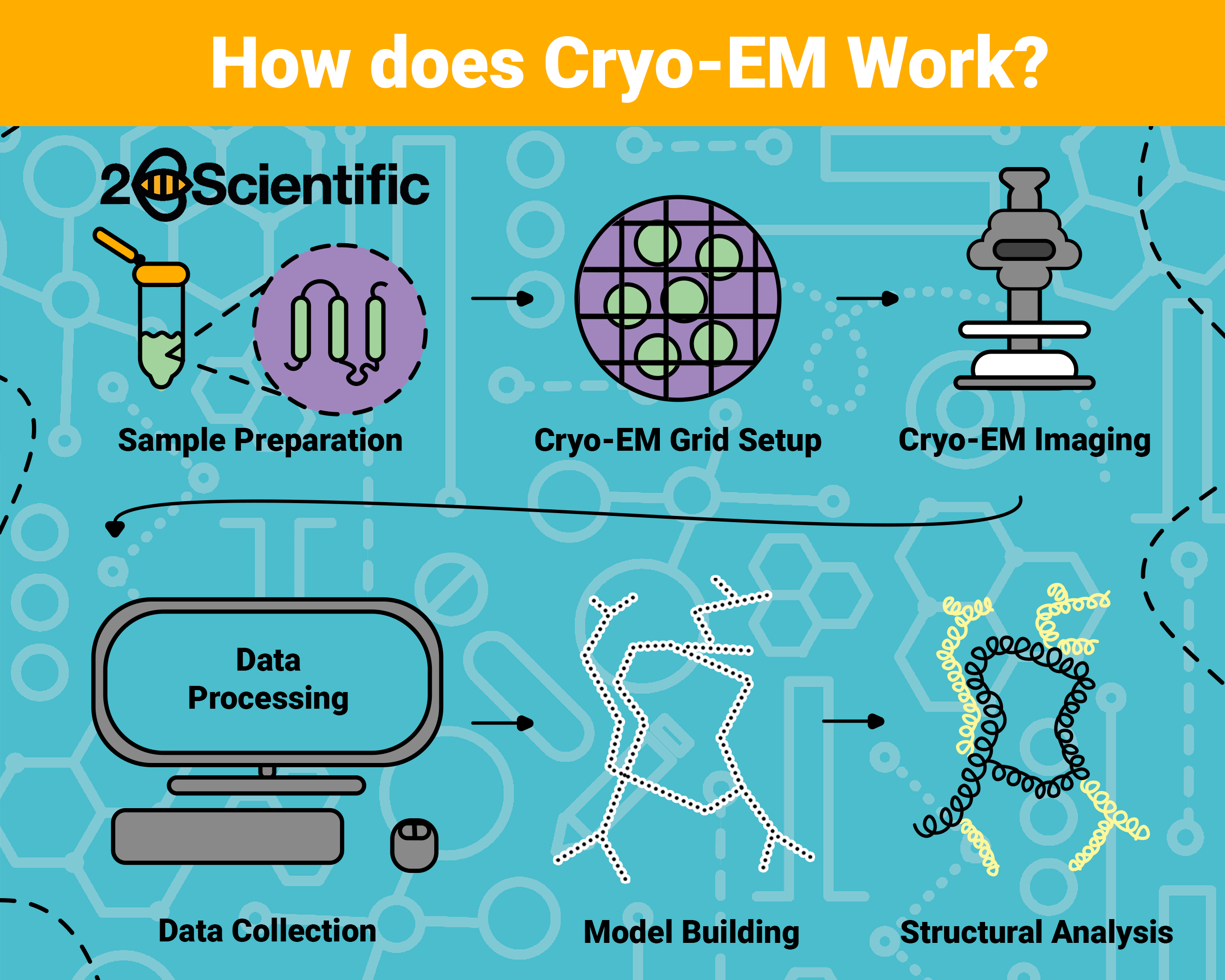
Cryo-EM
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a technique used to determine the structure of biological molecules at near-atomic resolution. The process involves rapidly freezing a sample to preserve its natural state and then imaging it using an electron microscope. The sample is bombarded with electrons, and the resulting images are collected.
The images are then processed using specialised software to create a three-dimensional model of the molecule. By combining multiple images taken from different angles, researchers can reconstruct the structure with extreme precision.
The benefits of cryo-EM for research include providing detailed structural information without the need for crystallisation, making it suitable for studying complex and flexible molecules that are difficult to crystallise. Cryo-EM is essential for understanding the function of large biomolecules, such as proteins and viruses, and is widely used in drug development, structural biology, and virology. This technique has revolutionised the field by allowing scientists to visualise molecular structures in their native environment, leading to new insights and advancements in various research disciplines.